
Original (left) and denoised (right) images. The image was denoised while preserving the edges using a wavelet denoising function.
You can use discrete wavelet transforms to perform multiresolution analysis and split signals into physically meaningful and interpretable components. This makes DWT useful for compressing and denoising signals and images while preserving important features. With the discrete wavelet transform scales are discretized more coarsely than with CWT. The short-time Fourier transform (center) does not clearly distinguish the instantaneous frequencies, but the continuous wavelet transform (right) accurately captures them. The continuous wavelet transform can be used to analyze transient behavior, rapidly changing frequencies, and slowly varying behavior.Īnalyzing a hyperbolic chirp signal (left) with two components that vary over time in MATLAB. The window widens in time, making it suitable for low-frequency phenomena, and narrows for high-frequency phenomena. The STFT uses a fixed window to create a local frequency analysis, while CWT tiles the time-frequency plane with variable-sized windows. CWT is similar to the short-time Fourier transform (STFT).

A signal being nonstationary means that its frequency-domain representation changes over time. The continuous wavelet transform is a time-frequency transform, which is ideal for analysis of non-stationary signals. Wavelet transforms can be classified into two broad classes: the continuous wavelet transform (CWT) and the discrete wavelet transform (DWT). Sorry, your browser doesn't support embedded videos.Ĭapturing transient behavior in signals using a MATLAB wavelet transform. For both signals and images, the smooth regions and transients can be sparsely represented with wavelet transforms. Similarly, images typically include homogenous, piecewise smooth regions separated by transients, which appear as edges.
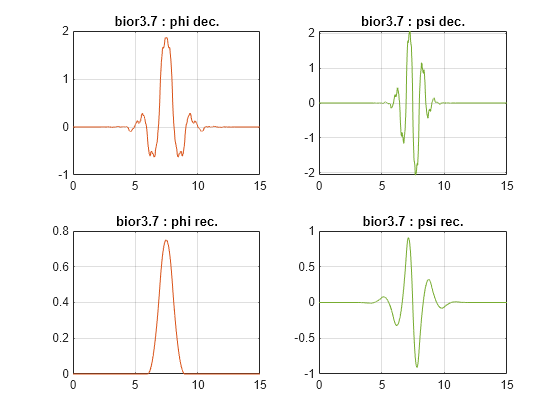
Wavelet Toolbox™ for use with MATLAB ® supports Morlet, Morse, Daubechies, and other wavelets used in wavelet analysis.Īudio signals, time-series financial data, and biomedical signals typically exhibit piecewise smooth behavior punctuated by transients. Different wavelets can be used depending on the application. This enables wavelets to represent data across multiple scales. A wavelet, unlike a sine wave, is a rapidly decaying, wave-like oscillation. While Fourier analysis consists of decomposing a signal into sine waves of specific frequencies, wavelet analysis is based on decomposing signals into shifted and scaled versions of a wavelet. Wavelet transforms were primarily created to address limitations of the Fourier transform. For images, features include edges and textures.

For signals, features can be frequencies varying over time, transients, or slowly varying trends. Wavelet transforms are mathematical tools for analyzing data where features vary over different scales. Soon you will see how easy it is to do this in MATLAB. Our goal here is to denoise the noisy signal using the discrete wavelet transform. There are two signals here: The first is the original signal, and the second one is the original signal with some noise added to it. Let us load a signal and plot it in MATLAB. This construction leads us to a new wavelet transform, called the empirical wavelet. The main idea is to extract the different modes of a signal by designing an appropriate wavelet filter bank. The implementation of the periodic discrete wavelet transform on MATLAB is explained.
#Wavelet matlab code pdf#
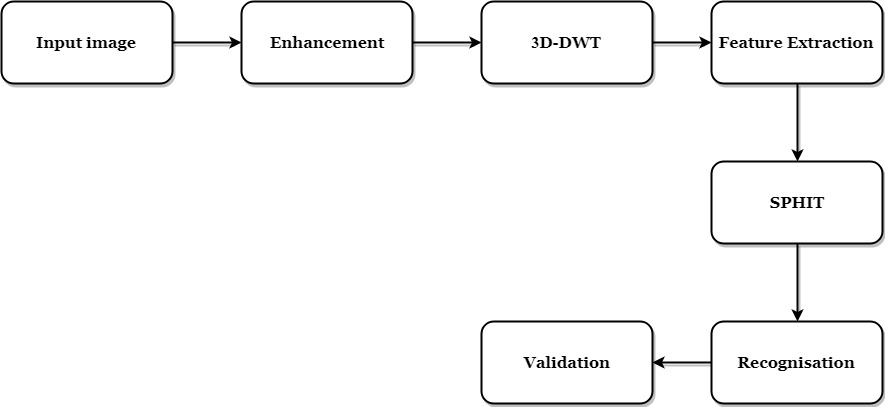
Analyze signals and images in the wavelet domainĭownload full-text PDF Read full-text.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
